Introduction
Man’s basic drive is for food to satisfy his hunger. Food is intimately woven into the physical, economical, psychological, intellectual and social life of man. It is a part of his culture and is filled with many different meanings and symbolism's for all individuals at various ages and stages of their maturity.
Food is source of power.
Food is source of security.
Food is a status symbol.
Food is a symbol of hospitality and friendship throughout the world. (We offer our hospitality to guest through an offer of food or a drink)
Food is an outlet for emotion.
Introduction
The food industry, be it the processing industry or the catering industry is one of the largest and most needed industry in the world today, fulfilling one of our basic need, ie; food.
Development of food industry can be traced back with various examples of food preservation, being time immemorial. Improvement in equipment and machinery has made possible to increase the capacity of food processing plants.
The aesthetic value of food of food is important. To be able to offer the consumer quality cuisine, basic knowledge of food science and its application is necessary. Every food handler should know foods composition, structure, behavior and the changes that takes place during cooking, holding and storage as well as what happens to food once it is consumed ie, its digestion , absorption, and metabolism in the human body.
Food is defined as anything solid or liquid which when swallowed, digested and assimilated and nourishes the body.
Food science is a systematic study of the nature of food materials and the scientific principles underlying their modification, preservation and spoilage.
Study of the characteristics of foods including chemical properties, biochemical properties, physical properties, and effects of these on the quality of products it also covers application of this information to development of new products and efficient food processing techniques. (Dictionary of food science).
Definition
It is a discipline in which the biological and physical sciences and engineering are used to study the nature of foods, the causes of their deterioration, and the principles underlying food processing. It deals with acquisition of new knowledge to elucidate the course of reactions or changes occurring in foods whether natural or induced by handling procedures.
Food is a mixture of many different chemical components. The study of food science involves an understanding of the changes that occur in these components during food preparation whether natural or induced by handling procedures many physical and chemical reaction occur during food preparation these reactions may be a result of the interaction between components with the medium of cooking, and the environmental conditions like heat cold light and air to which they are subjected during cooking.
Study of food science also includes understanding the nutritive value of different foods and methods of preserving them during cooking this information provides a foundation of theory and method on which they build the study of food preparation.
With liberalization of Indian economy, all-round industrial growth has been witnessed in all sectors with improvement in social and economic conditions of our people.
This has created demand for more and better quality foods. With advancement in production technology, high yield levels will lead to large amount of marketable surplus of food grains and crop residues, demanding appropriate handling, processing, preservation, storage, marketing and utilization.
The development of processing industries to preserve the perishable agricultural produce will not only improve economic and nutritional status of our population but it may help in employment generation in rural as well as urban areas of the country.
Scope of Food Science
The importance of food science lies in the fact that it has capability to provide food to our population through scientific conservations, eliminating avoidable losses and making available more balanced and nutritious food.
High value products from low grade material can be produced by innovative and appropriate processing and packaging technologies and also from by-products and residue waste using integrated approach.
The role of food technologist does not stop at farm level but it continues till the harvested crops and animal products are processed, preserved and further modified into useful and nutritious products, until it is utilized by the consumer.
Moreover, with development of processing industries, it is quite likely that the demand for food scientists and technologists will increase in the next few decades.
Food Science and its relation with other Sciences
To understand food science the basic concepts of physics, chemistry, biology, mathematics and their applications ie. Biochemistry, microbiology and food technology are necessary to prepare, package, store and serve wholesome high quality products.
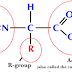
All foods are chemical compounds which undergo various chemical reactions at all stage from production to consumption These reactions are based on the laws of chemistry. Many processes used while preparing food involve physical changes apart from chemical changes.
There are 3 states of matter – Gases, Liquid, Solids.
As temperature is increased or decreased Solids get converted to Liquid which further converts to Gases, with change in chemical compounds. But decomposition of organic compounds place , undergoing various chemical reactions take place instead of change in state when temperature is raised.
Many foods are complex mixtures of chemical substances. In processed foods additives are added to improve colour, texture, flavour etc. These additives are chemical compounds. It undergoes further chemical changes during storage, cooking, processing as well as in the human body during digestion of food by action of chemical substances
During preparation and storage food is subjected to various physical conditions which affects its quality eg. temperature and pressure changes.
It is the science that deals with the composition, structure and properties of food and with chemical changes that take place in food.
It forms a major part of food science and is closely related to food microbiology
The chemical composition of food tells which micro-organism can grow on it and the changes that take place in the food because of their growth.
Changes can be desirable and undesirable which can lead to contamination of the food and further leading to food poisoning, food infection or just spoiling of the food rendering it unfit for consumption.
Microbiology is the study of micro organisms. Micro organisms are very small, usually single celled organisms which are not individually visible to the naked eye. If they are present in large number in food can lead to food poisoning. They are being used by man for production of certain foods eg. bread and yoghurt.
Interactions between Micro-organisms, plants and animals are natural and constant. Since the human food supply consists basically and animals or products derived from them, it is understandable that our food supply can contain micro-organisms in interaction with the food.
A knowledge of the factors that favors or inhibit the growth of Micro -organisms is essential to an understanding of the principle of food spoilage and preservation.
Food chemistry and food microbiology are intimately related to food processing because the processes to which food needs to be subjected to improve its texture, flavor and aroma depend on its composition and ingredients. The time and temperature for food processing depends not only on the chemical composition of food but on its microbial load and the type of packaging to be used.
The growing public demand for meals away from home has made the problem of serving safe, wholesome food more critical and challenging. This makes it imperative for food handlers to understand and implement the basic principles of the food science to enable them to prepare and serve high quality products over extended hours.
Rapid urbanization has lead to increase in demand of convenience foods (foods that require little labor and time to prepare eg. frozen peas). To these food additives are added to restore properties and to bring certain changes for storage. The special requirements for them are:
They need to be handled properly.
Not to be stored in open.
Maintenance of hygienic condition.
Similarly numerous food choices exist like canned foods, snacks, soups etc.
Thus food science covers all the aspects of food from properties of food materials and influences of all factors affecting food, beginning from growing the food to harvesting or slaughter i.e. all stages, from raw till it is consumed like processing, nutritive value, shelf life, novel sources of food, fabricated food and food analogs, conservation and re-use of resources to make more food.
Hence we can say that study of food science will be of benefit to all food professionals.
Man’s basic drive is for food to satisfy his hunger. Food is intimately woven into the physical, economical, psychological, intellectual and social life of man. It is a part of his culture and is filled with many different meanings and symbolism's for all individuals at various ages and stages of their maturity.
Food is source of power.
Food is source of security.
Food is a status symbol.
Food is a symbol of hospitality and friendship throughout the world. (We offer our hospitality to guest through an offer of food or a drink)
Food is an outlet for emotion.
Introduction
The food industry, be it the processing industry or the catering industry is one of the largest and most needed industry in the world today, fulfilling one of our basic need, ie; food.
Development of food industry can be traced back with various examples of food preservation, being time immemorial. Improvement in equipment and machinery has made possible to increase the capacity of food processing plants.
The aesthetic value of food of food is important. To be able to offer the consumer quality cuisine, basic knowledge of food science and its application is necessary. Every food handler should know foods composition, structure, behavior and the changes that takes place during cooking, holding and storage as well as what happens to food once it is consumed ie, its digestion , absorption, and metabolism in the human body.
Definition
Food is defined as anything solid or liquid which when swallowed, digested and assimilated and nourishes the body.Food science is a systematic study of the nature of food materials and the scientific principles underlying their modification, preservation and spoilage.
Study of the characteristics of foods including chemical properties, biochemical properties, physical properties, and effects of these on the quality of products it also covers application of this information to development of new products and efficient food processing techniques. (Dictionary of food science).
Definition
It is a discipline in which the biological and physical sciences and engineering are used to study the nature of foods, the causes of their deterioration, and the principles underlying food processing. It deals with acquisition of new knowledge to elucidate the course of reactions or changes occurring in foods whether natural or induced by handling procedures.
Food is a mixture of many different chemical components. The study of food science involves an understanding of the changes that occur in these components during food preparation whether natural or induced by handling procedures many physical and chemical reaction occur during food preparation these reactions may be a result of the interaction between components with the medium of cooking, and the environmental conditions like heat cold light and air to which they are subjected during cooking.
Study of food science also includes understanding the nutritive value of different foods and methods of preserving them during cooking this information provides a foundation of theory and method on which they build the study of food preparation.
Scope of Food Science
With liberalization of Indian economy, all-round industrial growth has been witnessed in all sectors with improvement in social and economic conditions of our people.This has created demand for more and better quality foods. With advancement in production technology, high yield levels will lead to large amount of marketable surplus of food grains and crop residues, demanding appropriate handling, processing, preservation, storage, marketing and utilization.
The development of processing industries to preserve the perishable agricultural produce will not only improve economic and nutritional status of our population but it may help in employment generation in rural as well as urban areas of the country.
Scope of Food Science
The importance of food science lies in the fact that it has capability to provide food to our population through scientific conservations, eliminating avoidable losses and making available more balanced and nutritious food.
High value products from low grade material can be produced by innovative and appropriate processing and packaging technologies and also from by-products and residue waste using integrated approach.
The role of food technologist does not stop at farm level but it continues till the harvested crops and animal products are processed, preserved and further modified into useful and nutritious products, until it is utilized by the consumer.
Moreover, with development of processing industries, it is quite likely that the demand for food scientists and technologists will increase in the next few decades.
Food Science and its relation with other Sciences
To understand food science the basic concepts of physics, chemistry, biology, mathematics and their applications ie. Biochemistry, microbiology and food technology are necessary to prepare, package, store and serve wholesome high quality products.
All foods are chemical compounds which undergo various chemical reactions at all stage from production to consumption These reactions are based on the laws of chemistry. Many processes used while preparing food involve physical changes apart from chemical changes.
Food Science and its relation with other Sciences
There are 3 states of matter – Gases, Liquid, Solids.As temperature is increased or decreased Solids get converted to Liquid which further converts to Gases, with change in chemical compounds. But decomposition of organic compounds place , undergoing various chemical reactions take place instead of change in state when temperature is raised.
Many foods are complex mixtures of chemical substances. In processed foods additives are added to improve colour, texture, flavour etc. These additives are chemical compounds. It undergoes further chemical changes during storage, cooking, processing as well as in the human body during digestion of food by action of chemical substances
During preparation and storage food is subjected to various physical conditions which affects its quality eg. temperature and pressure changes.
Food chemistry
It is the science that deals with the composition, structure and properties of food and with chemical changes that take place in food.
It forms a major part of food science and is closely related to food microbiology
The chemical composition of food tells which micro-organism can grow on it and the changes that take place in the food because of their growth.
Changes can be desirable and undesirable which can lead to contamination of the food and further leading to food poisoning, food infection or just spoiling of the food rendering it unfit for consumption.
Food Microbiology
Microbiology is the study of micro organisms. Micro organisms are very small, usually single celled organisms which are not individually visible to the naked eye. If they are present in large number in food can lead to food poisoning. They are being used by man for production of certain foods eg. bread and yoghurt.
Interactions between Micro-organisms, plants and animals are natural and constant. Since the human food supply consists basically and animals or products derived from them, it is understandable that our food supply can contain micro-organisms in interaction with the food.
A knowledge of the factors that favors or inhibit the growth of Micro -organisms is essential to an understanding of the principle of food spoilage and preservation.
Food chemistry and food microbiology are intimately related to food processing because the processes to which food needs to be subjected to improve its texture, flavor and aroma depend on its composition and ingredients. The time and temperature for food processing depends not only on the chemical composition of food but on its microbial load and the type of packaging to be used.
Food Processing
The growing public demand for meals away from home has made the problem of serving safe, wholesome food more critical and challenging. This makes it imperative for food handlers to understand and implement the basic principles of the food science to enable them to prepare and serve high quality products over extended hours.
Rapid urbanization has lead to increase in demand of convenience foods (foods that require little labor and time to prepare eg. frozen peas). To these food additives are added to restore properties and to bring certain changes for storage. The special requirements for them are:
They need to be handled properly.
Not to be stored in open.
Maintenance of hygienic condition.
Similarly numerous food choices exist like canned foods, snacks, soups etc.
Conclusion
Thus food science covers all the aspects of food from properties of food materials and influences of all factors affecting food, beginning from growing the food to harvesting or slaughter i.e. all stages, from raw till it is consumed like processing, nutritive value, shelf life, novel sources of food, fabricated food and food analogs, conservation and re-use of resources to make more food.
Hence we can say that study of food science will be of benefit to all food professionals.


No comments:
Post a Comment